Latitudes and Longitudes
Before seeing about time zones, let's refresh our knowledge of Geography to know about latitudes and longitudes.
A point on a circle can be located by specifying a number, i.e. an angle from a particular line of reference (this line is one of the radii of the circle). But to identify a point on a circle, we need two angles.
The earth's surface is spherical and thus requires two angles to specify a point on its surface. This is where Latitudes and longitudes come in.
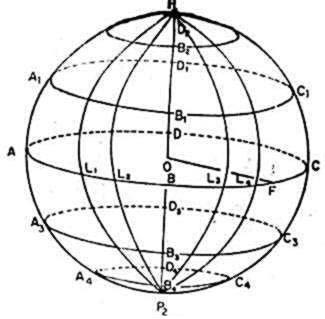
Consider a plane passing through the center of the circle and perpendicular to the line joining the north and south poles. This plane will cut the surface of the earth in a circle whose radius is equal to the radius of the earth. This circle is called the Equator. The plane containing the Equator is the equatorial plane, which divides the earth into two hemispheres. The part of the earth above the equator, i.e. towards the North Pole, is called the Northern Hemisphere. The part of the earth below the equator, i.e. towards the South Pole is called the Southern Hemisphere.
Many planes can be drawn parallel to the equatorial plane which cut the earth in circles with radius smaller than that of the equator. These circles are called latitude circles or simple latitudes.
In the figure shown above, we can see semicircular arcs, which join the North Pole to the South Pole. These circles are called meridians. Every point on the earth's surface will lie on one meridian or the other.
We can cover the entire earth's surface with latitudes and meridians. Every point on the earth will lie on a particular meridian and a particular latitude. The latitude of a place is the angle between the line drawn from that point to the center of the earth and the equatorial plane. The different points on a meridian have different latitudes. The latitude of a point can have any value between 0° to 90°. The latitudes are also classified as north and south (N or S) to differentiate between places to the north and south of the equator. The North Pole has a latitude of 90° and the South Pole has a latitude of 90° south.
The equator has a latitude of 0°. This is the reference latitude. Similarly a reference meridian is also required. By convention, the meridian passing through Greenwich, a place near London, is chosen as the reference meridian. The longitude of a point is the angle between the meridian passing through that point and the meridian passing through Greenwich. One should also specify whether the point is the east or west of Greenwich. Thus the longitude of a place may be anywhere from 0° to 180 ° E or W.Note that 180 ° E is the same as 180° W.
Thus any point on the surface of the earth can be pinpointed, if we are given its latitude & longitude values. For e.g.: Madras lies on the meridian and the latitude.
Proceed to time-zones